1
ORDER RECEIPT
Weighing the equipment and identifying references.
2
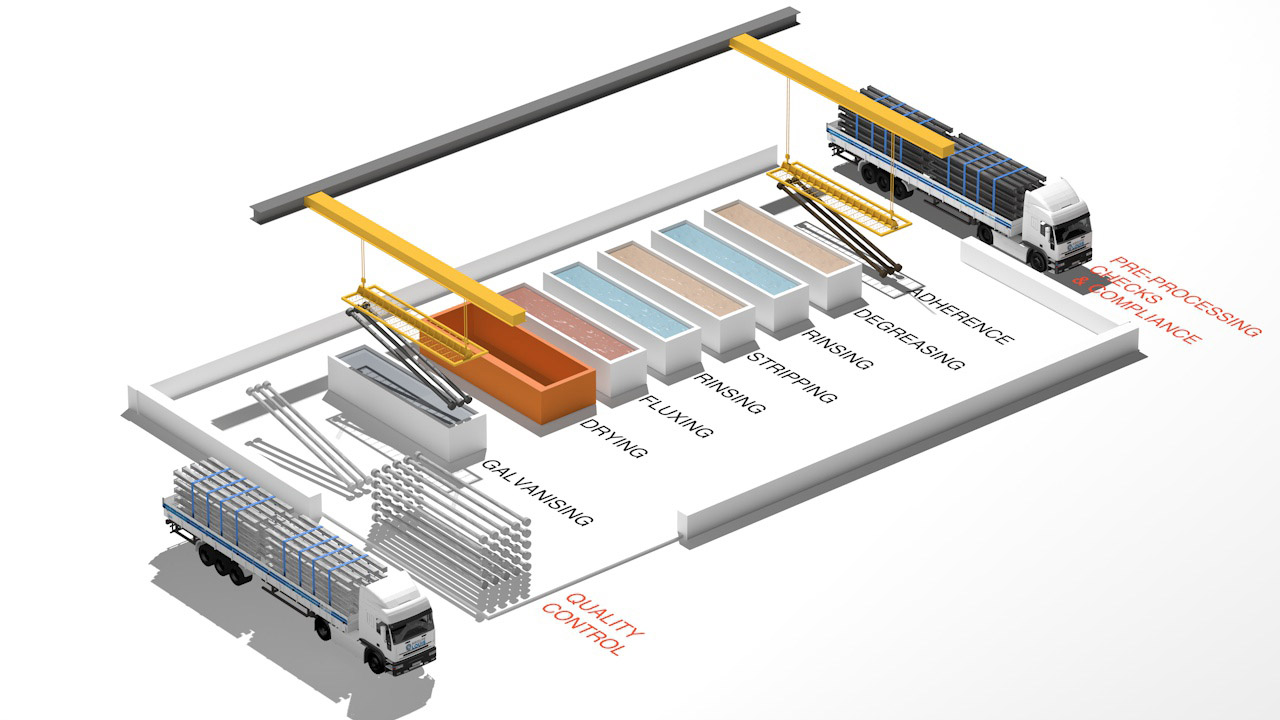
PRE-PROCESSING CHECKS & COMPLIANCE
Checking the products’ aptitude for galvanisation:
Surface condition, dimensions, design, drilling.
Quantitative checks in line with the customer’s purchase order.
Customer’s contact details in case of compliance-related measures.
3
ADHERENCE
Use of well-adapted tools according to the parts in question (round bars, chains, multiple hooks, etc.).
Optimising drilling positions.
4
DEGREASING
Its purpose is to remove all dirt and grease that would prevent surface iron oxides from dissolving.
5
RINSING
Rinsing occurs after he degreasing process so as not to pollute the following stages.
6
STRIPPING
Its purpose is to remove carbon deposits and other oxides on the steel’s surface.
Stripping is done using a hydrochloric acid solution diluted at room temperature, with added inhibiting agents to avoid the steel being attacked once the oxides have been removed.
7
RINSING
Another rinsing phase is launched after the stripping, to wash the iron salts and acid traces from the parts, as they may pollute the next stage.
8
FLUXING
This helps avoid the steel from re-oxidising before being plunged into the zinc bath. Decomposing the flow helps enhance the iron/zinc metal reaction when delving the part into the zinc bath.
9
DRYING
Drying is carried out in an oven, to avoid zinc projections when the part is plunged in.
10
GALVANISING
The parts are then plunged in a molten zinc bath at 450°C. Immersion times vary according to the loads, dimensions and thickness of the parts: 3 to 4 minutes for parts with simple shapes, 10 to 15 minutes for more massive products or large-size hollow entities.
11
COOLING & QUALITY CONTROL
Visual control upon removal from the zinc bath (aspect, distortion, etc.).
Testing thickness in comparison with a sample.
Delivery of a control report upon request, completed in line with the NF EN ISO 1461 standard.